logic之XHR hook拦截流程
因为各个api hook中,XMLHttRequest 的拦截最复杂,因此这里先介绍这个拦截原理。
流程图
我们先看下拦截到之后,我们fetBlockLogic中应当如何根据配置去拉取数据。流程图如下:
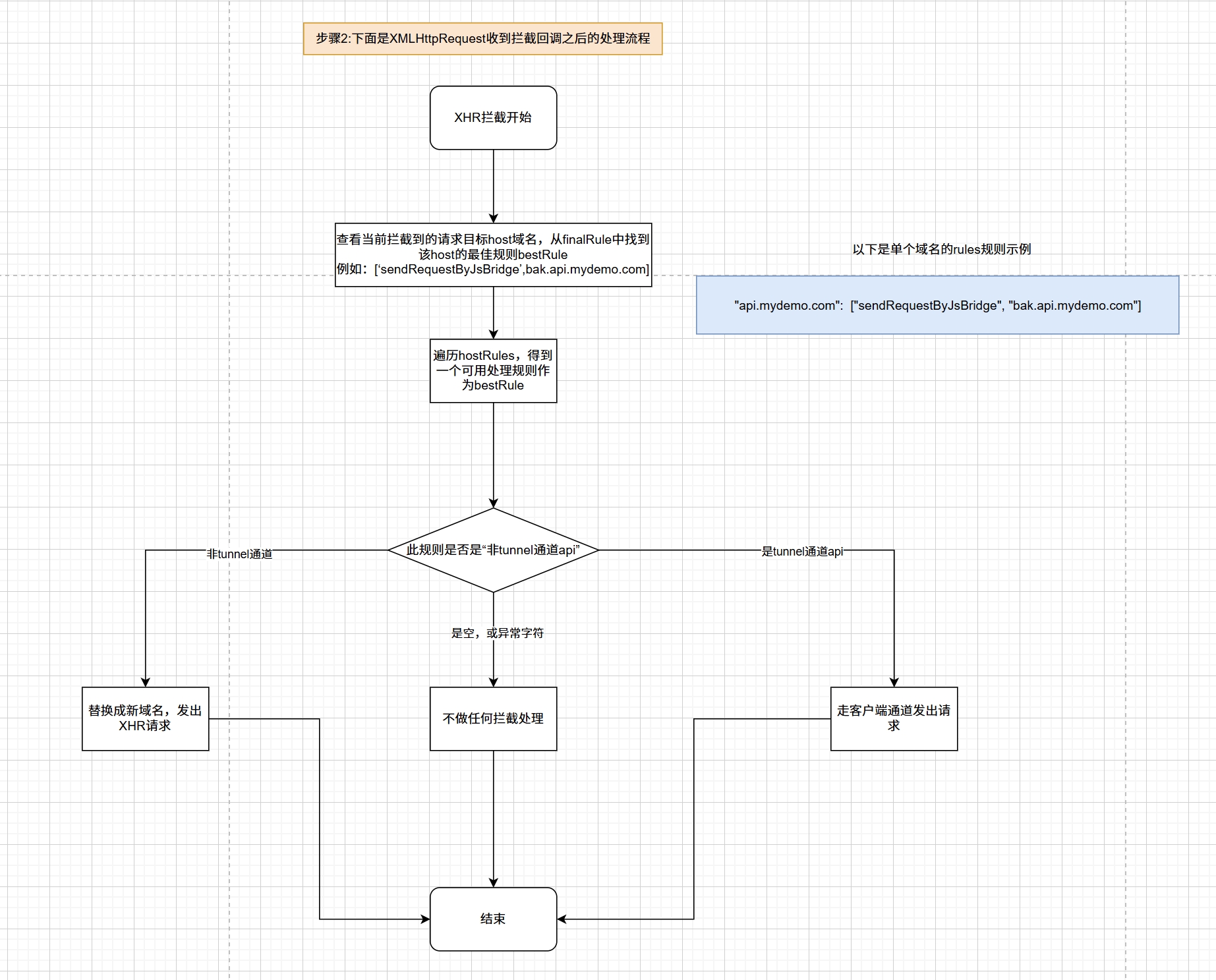
其实逻辑也相对简单,大概就是:
- 根据请求的url找出最佳规则。这个获取bestRule的过程,我们在前面章节已经讲过了。
- 根据计算出的bestRule发出请求。假如是原生xhr请求则用原生xhr发出,假如需要走tunnel特殊通道,则通过调用客户端jsbridge等技术完成,完成后需要完全模拟XHR的行为,从而让上层调用者无感知。
XHR api拦截的具体实现
为了能保持xhr上层api无感,底层可以实现多通道支持。我们采用继承原生 window.XMLHttpRequest class 的方式。继承后,对 XMLHttpRequest 的所有api进行覆盖实现。
继承并重写父类相关api的代码如下(合计218行代码):
Details
js
import { getRuleByRequestUrl } from '../rulesManager/index.js'
import { sendRequestByTunnel } from '../tunnels/index.js'
// 实现fetBlock封装后的 XMLHttpRequset class
export class FetBlockXMLHttpRequest extends window.XMLHttpRequest {
// 静态属性
static isFetBlockXHR = true
static fetBlockVersion = pkgVersion
// 实例属性
#status = 0 // 模拟xhr http报文响应状态
#statusText = '' // 模拟xhr http报文响应文本
#readyState = 0 // 模拟xhr响应进度状态
#responseText = '' // 模拟xhr响应内容
#responseHeaders = {} // 模拟xhr响应头
#responseURL = '' // 模拟xhr响应url
// fetBlockXHR内部私有变量
#tunnelType = '' // 模拟xhr请求类型
#isAbort = false // 标记是否取消此次请求
#requestHeaders = {} // 存储xhr请求头
#openArgs = null // 存储open时候的参数
constructor() {
super()
}
get status() {
if (this.#tunnelType !== 'xhr') return this.#status
return super.status
}
get statusText() {
if (this.#tunnelType !== 'xhr') return this.#statusText
return super.statusText
}
get readyState() {
if (this.#tunnelType !== 'xhr') return this.#readyState
return super.readyState
}
get responseText() {
if (this.#tunnelType !== 'xhr') return this.#responseText
return super.responseText
}
get responseHeaders() {
if (this.#tunnelType !== 'xhr') return this.#responseHeaders
return super.responseHeaders
}
get responseURL() {
if (this.#tunnelType !== 'xhr') return this.#responseURL
return super.responseURL
}
get response() {
if (this.#tunnelType !== 'xhr') {
if (this.responseType === 'json') {
return JSON.parse(this.#responseText)
}
else {
return this.#responseText
}
}
return super.response
}
open(method, url, async = true, username, password) {
this.#resetXhrStatus()
if (!method || !url) {
throw new Error('method and url are required')
}
// 无论走什么通道,都要先用原生xhr open一下,因为open之后,才能调用setRequestHeader这类api
super.open(method, url, async, username, password)
this.#openArgs = {
method, url, async, username, password
}
// 模拟原生行为,更新readyState
this.#readyState = 1
}
send(bodyData) {
const bestRule = getRuleByRequestUrl(this.#openArgs)
console.log('最佳规则为:', bestRule)
if (!bestRule) return super.send()
this.#tunnelType = bestRule.type
// 原始xhr通道
if (this.#tunnelType !== 'tunnel') {
// 由于替换过了域名,因此需要再次open一次
super.open(this.#openArgs.method, bestRule.targetUrl, this.#openArgs.async, this.#openArgs.username, this.#openArgs.password)
Object.keys(this.#requestHeaders).forEach(k => {
super.setRequestHeader(k, this.#requestHeaders[k])
})
return super.send(bodyData)
}
// 特殊通道则调用特殊通道来完成请求
const tunnelApi = bestRule.tunnelApi
const requsetPromise = sendRequestByTunnel({
...this.#openArgs,
url: bestRule.targetUrl,
body: bodyData
}, tunnelApi)
this.dispatchEvent(new ProgressEvent('loadstart', {
loaded: 0,
total: 0
}))
requsetPromise.then(res => {
if (this.#isAbort) return
let loaded = 0
let total = 100
if (typeof res === 'object' && res?.body && typeof res?.body === 'string') {
loaded = res?.body?.length
total = res?.body?.length
}
this.dispatchEvent(new ProgressEvent('progress', {
loaded,
total
}))
this.#readyState = 4
this.#status = res.status || 200
this.#statusText = res.statusText || 'TUNNEL_REQUEST_OK'
this.#responseHeaders = res?.headers || {}
this.#responseText = res?.body
this.#responseURL = bestRule.targetUrl
this.dispatchEvent(new ProgressEvent('readystatechange'))
this.dispatchEvent(new ProgressEvent('load', {
loaded: res?.body?.length,
total: res?.body?.length
}))
console.log('xhr内部onload触发完成')
}).catch(err => {
if (this.#isAbort) return
this.#resetXhrStatus({
status: 0,
statusText: '',
readyState: 4
})
this.#responseText = ''
this.#responseHeaders = {}
this.#responseURL = ''
this.dispatchEvent(new ProgressEvent('error', {
loaded: 0,
total: 0
}))
this.dispatchEvent(new ProgressEvent('loadend', {
loaded: 0,
total: 0
}))
return err
}).then(res => {
if (this.#isAbort) return
let loaded = 0
let total = 100
if (typeof res === 'object' && res?.body && typeof res?.body === 'string') {
loaded = res?.body?.length
total = res?.body?.length
}
this.dispatchEvent(new ProgressEvent('loadend', {
loaded,
total
}))
})
// 发完tunnel请求后,立刻模拟readyState状态
this.#readyState = 2
this.dispatchEvent(new Event('readystatechange'))
}
getAllResponseHeaders() {
if(this.#tunnelType !== 'xhr') return getResponseHeadersStr(this.#responseHeaders)
return super.getAllResponseHeaders()
}
getResponseHeader(name) {
if(this.#tunnelType !== 'xhr') return this.#responseHeaders[name]
return super.getResponseHeader(name)
}
setRequestHeader(name, value) {
this.#requestHeaders[name] = value
super.setRequestHeader(name, value)
}
abort() {
this.#isAbort = true
super.abort()
this.#resetXhrStatus({
isAbort: true
})
if (this.#tunnelType !== 'xhr') {
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
this.dispatchEvent(new ProgressEvent('abort', {
loaded: 0,
total: 0
}))
})
}
}
#resetXhrStatus(resetParams = {}) {
const { readyState, status, statusText, isAbort } = resetParams
this.#status = status || 0
this.#statusText = statusText
this.#readyState = readyState || 0
this.#requestHeaders = {}
this.#responseText = ''
this.#responseHeaders = {}
this.#responseURL = ''
this.#tunnelType = 'xhr'
this.#isAbort = typeof isAbort === 'boolean' ? isAbort : false
}
}以上代码实现了: open、send、setRequestHeader、getAllResponseHeaders、getResponseHeader、abort 等方法。基本覆盖了一个 XHR 请求和响应所需的绝大多数 api。